CANONICAL FORMS ( SOP and POS)
CANONICAL FORMS
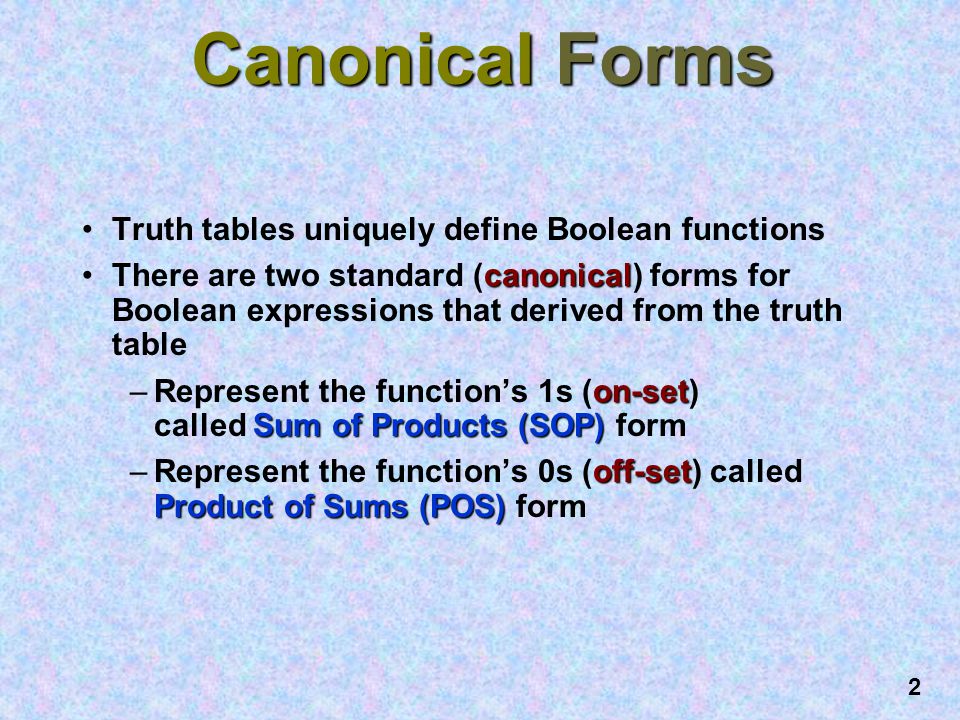
Two dual canonical forms of any Boolean function are a "sum of min terms" and a "product of max terms."

The term "Sum of Products" (SoP or SOP) is widely used for the canonical form that is a dis junction (OR) of min terms.
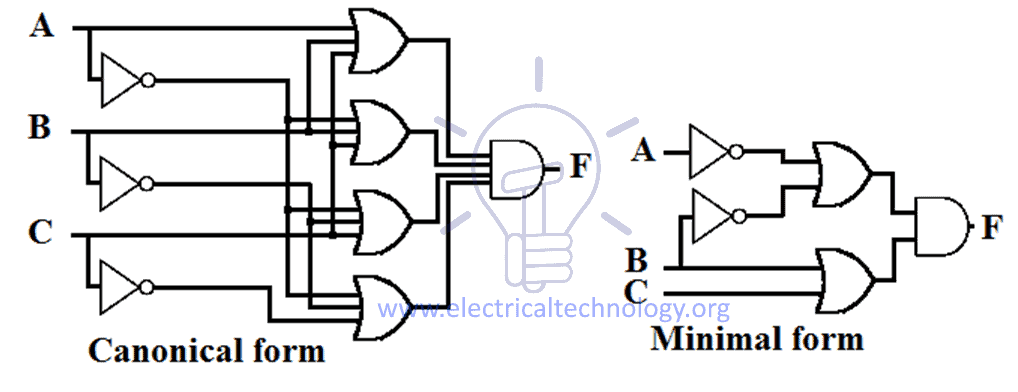
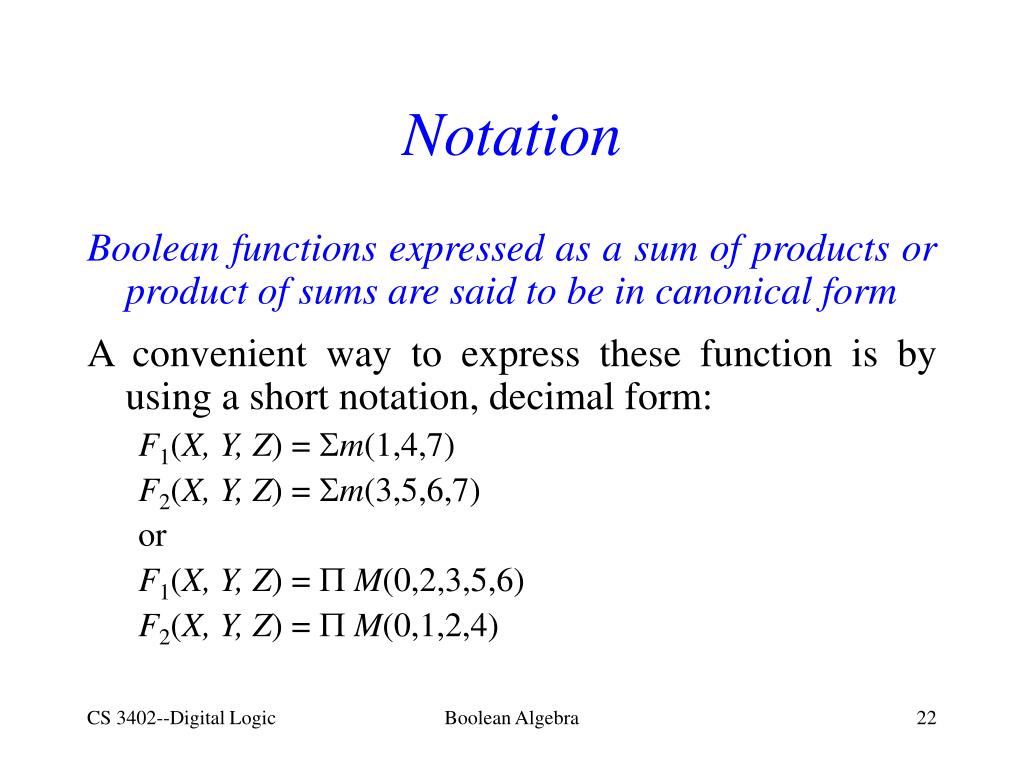
The SOP (Sum of Product) and POS (Product of Sum) are the methods for deducing a particular logic function. ...
The prior difference between the SOP and POS is that the SOP contains the OR of the multiple product terms. Conversely, POS produces a logical expression comprised of the AND of the multiple OR terms.
SOP Vs POS



CANONICAL FORMS OF SUM OF PRODUCT :
Canonical SoP form means Canonical form of Sum of Products. In this form, each product term contains all literals. So, these product terms are nothing but the min terms. Hence, canonical SoP form is also called as sum of min terms form.
CANONICAL FORM OF PRODUCT OF SUM
Canonical PoS form means Canonical Product of Sums form. In this form, each sum term contains all literals. So, these sum terms are nothing but the Max terms. Hence, canonical PoS form is also called as product of Max terms form.


Comments
Post a Comment